History
The Rajas of Hathras and Mursan both share common lineage to Nandram Thenua of Jawar the famous rebel ruler who revolted against the Mughal Emperor Aurangzeb. Nandram’s influence remained unimpaired until his death in 1695 A.D. He left fourteen sons, of whom only three need be mentioned here: Zulkaran, the eldest; Jai Singh, the second son; and Bhoj Singh, the seventh son. The Hathras family is descended from Raja Jai Singh, and that of Mursan from Zulkaran Singh. Zulkaran died before his father, and for some years, Bhoj Singh took the lead amongst the brethren. It is probable that the authority of Fauzdar Bhoj Singh varied just as he was able to secure the favor of the local Government officers. At last, in 1716 A.D., Bhoj Singh obtained from Sayyid Abdullah, the famous minister of Farrukhsiyar, a grant in terms similar to that conferred upon Nandram by Aurangzeb, and in the following year a remission of revenue as jagir. The two brothers, Jai Singh and Bhoj Singh, divided the tappa equally between them and transmitted their possessions to their sons. Bhoj Singh died in 1750 A.D. and left three sons. Of these, Mohan Singh obtained taluka Simardhari; Jagat Singh, the eldest son, received talukas Barha and Tuksan, and left Barha to his eldest son, Partab, whilst his second son, Muktwal Singh, received Tuksan and transferred it to Phup Singh of Mursan. Kanjal Singh, the third son of Bhoj Singh, received Chotwa and Kotha Patta, but he was ousted in 1768 on account of arrears, and the talukas were divided between the Hathras and Mursan Rajas.
We have now to trace the history of the family of Jai Singh. He died in 1749 A.D., and left two sons: Sawant Singh, the younger son, received a number of villages as his share, which he formed into a taluka named Tubrari; but the greater portion of the estate came into the hands of the eldest son, Baran Singh, a man of great vitality and determination of character. In 1752, Raja Baran Singh induced the amil of the Oudh Vazir to transfer to him the taluqa of Jalesar pargana and the surrounding villages, held until then by a clan of Porach Rajputs, and when Maharaja Surajmal, in 1760, expelled Ratan Singh, the Porach talukadar of Mendu, Baran Singh had influence enough to secure the revenue management for himself. Baran Singh died in 1768 and left two sons. The younger of these, by name Sakat Singh, succeeded to most of those villages included in his father’s estate which had formed a portion of the old tappa Joar. These were divided after his death into two smaller talukas, Karas and Karil – the former fell to the share of his son Durga Singh, and the second son, Udai Singh, obtained Karil. But all the individual acquisitions of Raja Baran Singh descended to his eldest son, Raja Bhuri Singh, who did not survive many years, and during whose time the estate appears neither to have increased nor diminished. Bhuri Singh died in 1775 A.D., and Dayaram, his youngest son, found means to supplant his elder brother, Nawal Singh, in by far the larger part of his father’s possessions. The latter retired to Beswan and founded the Beswan taluka.
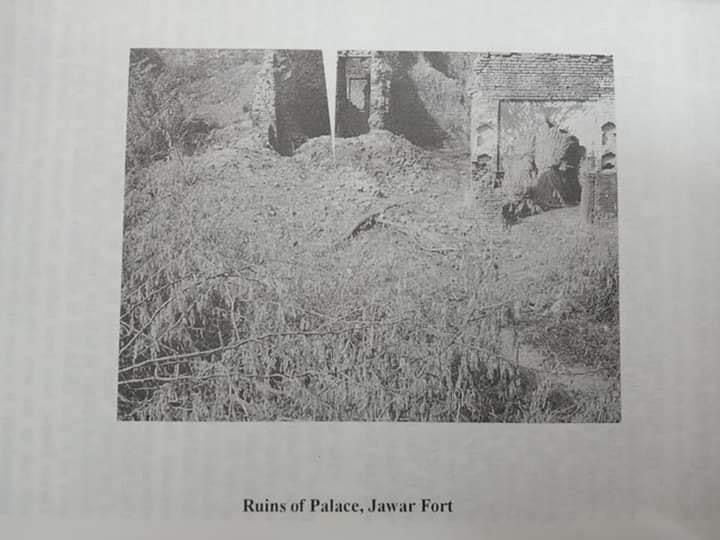
Dayaram was among the most powerful and influential rulers in the region, and his fort was said to be among the strongest in India. He was angered by the constant interference of the British administration in the affairs of his state and at the increasing revenue demands. Thus, he refused to pay revenue to the East India Company and also began providing shelter to rebels against the British Raj in his fort. After all attempts at negotiation broke down, the East India Company sent a powerful artillery force to besiege his fort. Dayaram and his loyal soldiers held out for several weeks. However, his fort was ultimately destroyed, and Dayaram, along with his followers, was captured and exiled.
Raja Govind Singh, son of Raja Dayaram, signed a treaty withthe British and took the Jamindari of nearly 120 villages(including the township of Koel) and started living in Vrindavan (today a part of Mathura). The adopted son of Shri Govind Singh named Shri Harnarayan Singh also remained a devotee of the British in Vrindavan. Shri Harnarayan Singh had no issue, so he adopted the third son of Raja Ghan Shayam Singh of Mursan state named Raja Mahendra Pratap later on, who a famous Freedom Fighter, the president of the first Indian National Government in exile and the first Noble peace prize nominee from India.
Genealogy
- Thakur Shri NANDRAM SINGH, Ruler of Jawar, Faujdar, married and had issue. He died 1696
- Raja Shri Jai Singh (qv)
- Thakur Zulkaran Singh, Thakur of Mursan, married and had issue (see Mursan)
- Raja Shri JAI SINGHji, Raja of Hathras 1696/1749, Faujdar, he divided the tappa of Jawar with his brother Thakur Bhoj Singh, he greaty expanded his patrimony, conquered Hathras in the 1716 from the Poruch clan, He was like his father appointed as Fauzdar in the Sarkar of Koel, In 1719 when there was a war between Nikosiyar and Shamsherkhan, He with his brothers helped Shamsherkhan, He had a crucial role in victory at Agra, married and had issue. He died 1749
- Raja Shri Badan Singh (qv)
- Thakur Sawant Singh, Thakur of Gubrari, married and had issue.(see Gubrari)
- Raja Shri BADAN/SADAN SINGH, Raja of Hathras 1749/1768, he through his military brilliance conquered the areas of Madanpur, Tatarpur,Aliya,Mitai, Lakhnu, and other taluqas from the
zamindars of Middle Doab, he joined Maharaja Surajmal of Bharatpur during his Koel expedition, He defeated the Raja of Dariyapur and annexed his properry, He also took control of Mendu which was formally held by the Rao Ratan Singh of Mendu, married and had issue. He died 1768.
- Raja Shri Bhure Singh [Boori Singh] (qv)
- Thakur Sakat Singh, Thakur of Karil, married and had issue.
- Thakur Durga Singh, Thakur of Karas(see Karas)
- Thakur Udai Singh, Thakur of Karil, married and had issue.(see Karil-Jatoi)
- Raja Shri BHURE SINGH, Raja of Hathras 1768/1775, established the famous Dauji temple at Hathras, married and had issue. He died 1775.
- Raja Shri Dayaram Singh (qv)
- Thakur Nawal Singh, Thakur of Beswan, married and had issue.
- Raja Hari Krishan Singh, Thakur of Beswan, married and had issue.(see Beswan)
- Thakur Jiwaram Singh, Thakur of Mendu, married and had issue. He died 1835.
- Thakur Randhir Singh, Thakur of Mendu, married and had issue. (see Mendu)
- Raja Shri DAYARAM SINGH, Raja of Hathras 1775/1841, he assumed the title of Raja after his accession, and greatly expanded his territory and bought progress and prosperity to his state,
and for a time was considered the most powerful chief in this part of the country, he was deposed by the British authorities and his state annexed in 1817, married and had issue. He died 1841.
- Raja Govind Singh (qv)
- Raja Shri GOVIND SINGH, Raja of Hathras 1841/1861, he adopted Kunwar Harnarayan Singh, son of Thakur Rup Singh of Jatoi, he succeeded on his father's death to only a portion of one
village as zamindar, but his loyalty to British interests during the 1857 Mutiny, enabled him to recover much of the Hathras estate; married Rani Sahib (name unknown) Kunwar, a daughter of Chaudhary Charan Singh, and sister of Chaudhary Ratan Singh, maternal uncle of Maharaja Jaswant Singh of Bharatpur, and had adoptive issue. He died 1861.
- Kunwar (name unknown) Singh (by Rani Sahib Kunwar), died young in 1861.
- Raja Harnarayan Singh (qv)
- Raja Shri HARNARAYAN SINGH, Raja of Hathras 1863/1896, born 7th December 1864, he succeeded by adoption, he adopted Kunwar Kharag Singh in 1889, the third son of Raja Bahadur
Ghanshyam Singh of Mursan (see above), married 1stly, Rani Swarup Kaur from Bharatpur, married 2ndly, Rani Hanumant Kaur of Dholpur, and had adoptive issue. He died 1896.
- Raja Mahendra Pratap Singh (qv)
- Raja Shri MAHENDRA PRATAP SINGH, Raja of Hathras 1896/1924, born 1st December 1886 in the Thenua gotra of the Jat Hindu princely estate of Mursan in Aligarh in Uttar Pradesh, as
Kunwar Kharag Singh of Mursan; popularly known as Aryan Peshwa, he was a freedom fighter, journalist, writer and revolutionary social reformist of India, college educated, he received his education under British headmasters and Muslim teachers from the Mohammedan Anglo Oriental College, Aligarh; he established a free indigenous technical institute, ‘Prem Mahavidyalaya’ in his palace at Vrindavan in 1909, he established the first Provisional Government of India at Kabul in Afghanistan, in 1915; declared a fugitive by the British
Government of India, his estate was forfeited and he left for Japan, on 7th September 1924 the estate was granted to his son; later he published the ‘World Federation Monthly Magazine’ in 1929; he formed the Executive Board of India in Japan in 1940; and returned to India in 1946; Member of Parliament 1957/1962; President of Indian Freedom Fighters’ Association; President
of All India Jat Mahasabha; journalist and prolific writer who wrote a large number of books on various topics; married 1stly, 1902, Rani Balbir Kaur, daughter of Tikka Sahib Balbir Singh Bahadur of Jind, died 1925, married 2ndly, a daughter of Sardar Bhagwant Singh, Rais-i-Azam of Bhadaur, and had issue, one son and one daughter. He died on 29th April 1979.
- Kumari Bakti Devi Kaur
- Raja Prem Pratap Singh (qv)
- Raja Shri PREM PRATAP SINGH, Raja of Hathras 1924/1947, born 1912, married (sep'd. 1946), Georgiana (an English lady), and had issue. He died 13th June 1947 in Vrindavan.
- Raja Amar Pratap Singh (qv)
- Kumari Sarla Kaur, born 1942.
- Raja Shri AMAR PRATAP SINGH, Raja of Hathras from 1947,born 4th January 1940 in Dehradun, married 1968, Rani Balbir Kaur, and has issue.
- Kumari Meeta Kaur
- Kunwar Charat Pratap Singh
- Kunwar Sharad Pratap Singh
- Jat Rulers of the Upper Doab, Jagbir Singh
- The Golden Book of India